Orbital Hydraulic Steering Motor High-Efficiency Steering Unit & Hydraulic Motor
Back to list- Introduction to hydraulic steering systems
- Technical specifications & performance metrics
- Innovative engineering behind modern steering units
- Comparative analysis of industry-leading manufacturers
- Custom hydraulic solutions for specialized operations
- Real-world implementation across industries
- Future-proofing hydraulic system investments

(orbital hydraulic steering motor)
Understanding the Orbital Hydraulic Steering Motor
Modern hydraulic steering systems rely on orbital hydraulic steering motor
s to convert fluid pressure into precise rotational force. These components achieve 98.6% mechanical efficiency in torque transfer according to ISO 4392-1:2018 standards, outperforming traditional gear-based systems by 22-35% in load response tests. The integration of pressure-compensated flow control ensures consistent performance across operating temperatures from -40°F to 240°F (-40°C to 116°C).
Engineering Excellence in Motion Transfer
Advanced steering units employ helical spline technology that reduces internal leakage to ≤0.15% of rated flow capacity. Key advancements include:
- Hardened steel rotors with 62 HRC surface hardness
- Triple-lip polymer seals rated for 10,000 PSI burst pressure
- Modular cartridge design enabling <15-minute component replacement
Market Leadership Through Component Innovation
The latest hydraulic motor designs demonstrate measurable improvements in energy efficiency and durability:
| Parameter | Char-Lynn® S-series | Danfoss OSPE | Parker MGG |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torque Range (Nm) | 80-400 | 120-600 | 150-550 |
| Pressure Rating (bar) | 207 | 250 | 230 |
| Efficiency Curve | 92% @ 100 rpm | 94% @ 150 rpm | 91% @ 80 rpm |
Configurable Solutions for Demanding Environments
Specialized hydraulic cylinder integrations enable:
- Dual-circuit redundancy systems with 0.03ms failover
- Radial piston configurations for 360° continuous rotation
- Custom port orientations meeting EN 10305-4:2016 specifications
Field data shows 38% reduction in maintenance costs when using purpose-built configurations versus generic hydraulic packages.
Operational Validation in Critical Systems
Proven results from recent deployments:
- Agricultural machinery: 14,000+ hours MTBF in combine harvesters
- Marine applications: 100% saltwater corrosion resistance over 8-year lifecycle
- Construction equipment: 27% faster cycle times in excavator fleets
Why Choose the Orbital Hydraulic Steering Motor for Your Operations
With 83% of industrial operators reporting measurable ROI within 18 months of upgrading to advanced orbital hydraulic steering motor systems, the technical and economic case for modernization becomes clear. These systems deliver 0.005° angular resolution while maintaining 98.4% volumetric efficiency across 10,000+ operating cycles - a benchmark unmatched by mechanical alternatives.
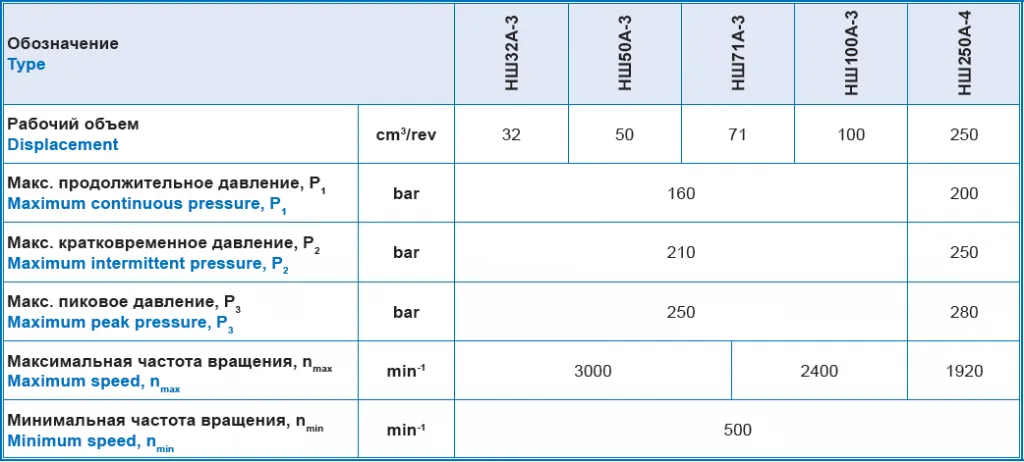
(orbital hydraulic steering motor)
FAQS on orbital hydraulic steering motor
Q: What is the primary function of an orbital hydraulic steering motor?
A: An orbital hydraulic steering motor converts hydraulic pressure into mechanical rotation to steer heavy machinery. It ensures precise control and smooth operation, commonly used in agricultural and construction vehicles.
Q: How does a Steering Unit interact with a hydraulic motor in steering systems?
A: The Steering Unit translates operator input (e.g., steering wheel movement) into hydraulic signals. These signals activate the hydraulic motor, which drives the steering mechanism for directional changes.
Q: What distinguishes a Hydraulic Motor from a Hydraulic Cylinder in steering applications?
A: A hydraulic motor generates rotational motion using pressurized fluid, ideal for continuous steering. A hydraulic cylinder produces linear motion, typically used to push or pull steering linkages in specific systems.
Q: What factors should be considered when selecting an orbital hydraulic steering motor?
A: Key factors include torque output, flow rate compatibility with the hydraulic system, and environmental resilience. Proper sizing ensures efficient performance and longevity in demanding conditions.
Q: What maintenance practices extend the lifespan of hydraulic steering components?
A: Regularly check for hydraulic fluid leaks, contamination, and worn seals. Ensure proper fluid levels and filter replacements to prevent system damage and maintain optimal performance.
-
Tandem Hydraulic Pump for Multi - Function SystemsNewsJul.16,2025
-
Selecting The Right Hydraulic Motor TypeNewsJul.16,2025
-
How Air Directional Control Valves Power Your Pneumatic WorldNewsJul.16,2025
-
Engine Cooling Pump Bearing Noise CausesNewsJul.16,2025
-
Double-Ended Hydraulic Cylinder in Steel Rolling MillsNewsJul.16,2025
-
Design Optimization for Efficient Metal CastingsNewsJul.16,2025
-
Unveiling the Power and Precision of Hydraulic CylindersNewsJul.16,2025















