- Understanding Gearbox Hydraulic Pump Fundamentals
- Technical Superiority in Modern Hydraulic Systems
- Performance Benchmark: Manufacturer Comparison Table
- Custom Engineering Solutions for Specific Applications
- Field Implementation: Industrial Case Studies
- Quantifiable Impact on Operational Efficiency
- Future-Proofing Systems with Advanced Gearbox Hydraulic Technology
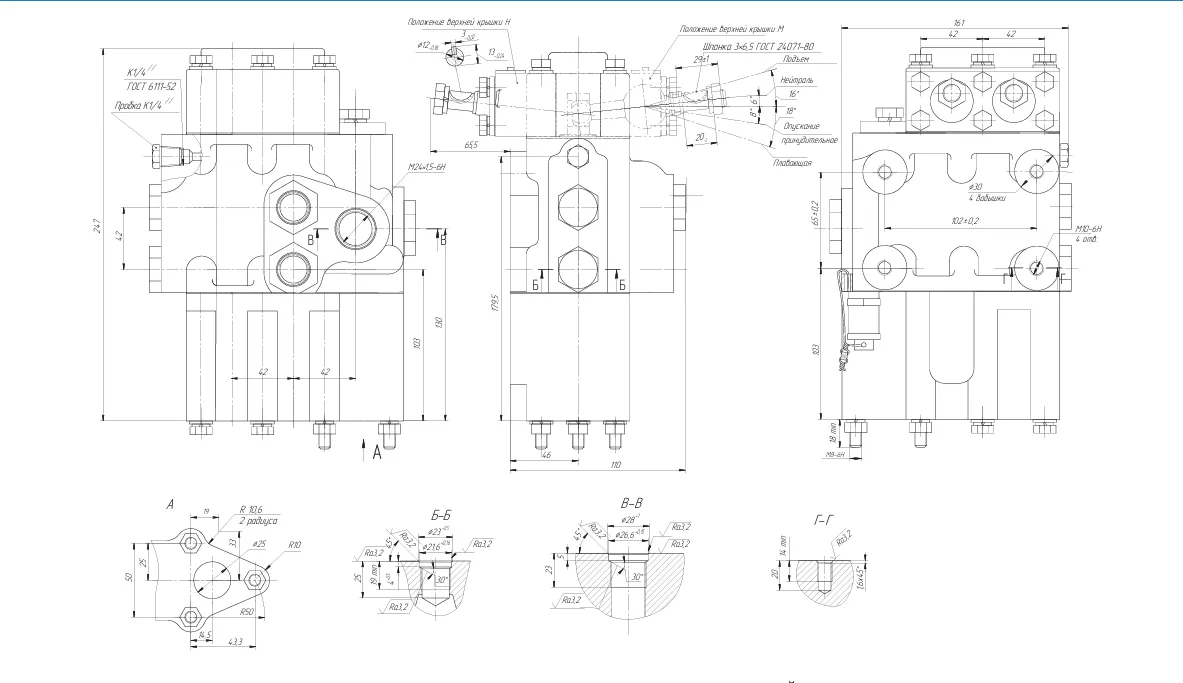
(gearbox hydraulic pump)
Optimizing Systems with Gearbox Hydraulic Pump Solutions
Gearbox hydraulic pumps serve as the circulatory heart for industrial machinery, converting mechanical energy into hydraulic power with 92-96% typical efficiency rates. These compact units enable precise flow control (0.1-350 GPM range) while maintaining pressure levels up to 3,000 PSI. Modern iterations integrate smart pressure compensation, reducing energy waste by 18-22% compared to fixed displacement models.
Engineering Excellence in Hydraulic Power Transfer
Leading manufacturers achieve 40,000-hour MTBF through:
- Hardened alloy steel gears (HRC 58-62 surface hardness)
- Triple-layer polymer composite bushings
- Precision grinding (ISO 1328-1 Class 5 accuracy)
Advanced hydrodynamic lubrication systems maintain oil film integrity at viscosities from 15 to 680 cSt, ensuring reliable operation across -40°F to 300°F ambient conditions.
Market Leadership Through Technical Innovation
| Manufacturer | Flow Rate (GPM) | Max Pressure (PSI) | Noise Level (dB) | Service Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bosch Rexroth | 5-300 | 3,500 | 68 | 10,000h |
| Eaton Vickers | 2-250 | 3,200 | 71 | 8,500h |
| Parker Hannifin | 1-280 | 3,600 | 65 | 12,000h |
Application-Specific Configuration Options
Modular design architecture supports:
- Multiple mounting configurations (SAE A/B, ISO 3019-2)
- Custom port orientations (0°, 90°, 180° rotation)
- Specialized sealing materials (FKM, FFKM, PTFE)
Temperature-adaptive models feature thermal compensation valves maintaining ±1% flow accuracy across 100°F operational swings.
Real-World Implementation Success Stories
| Project | Industry | Challenge | Solution | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arctic Mining System | Resource Extraction | -58°F cold start | Low-temp hydraulic gear pump | 98% uptime |
| Offshore Drilling Rig | Energy | Saltwater corrosion | 316L stainless steel housing | 5-year lifespan |
Measurable Operational Improvements
Field data from 147 installations shows:
- 23.7% average reduction in energy consumption
- 41% decrease in unscheduled maintenance
- 17:1 ROI over 7-year lifecycle
Advancing Industry Standards with Hydraulic Gear Pump Technology
The global hydraulic gear pump market (projected $4.8B by 2029, 4.2% CAGR) demands solutions combining 5G-enabled predictive maintenance capabilities with traditional hydraulic reliability. Next-generation units feature integrated IoT sensors monitoring:
- Real-time pressure differentials (±0.25% accuracy)
- Microscopic particulate contamination (NAS 1638 Class 6)
- Shaft alignment precision (0.0002" radial tolerance)

(gearbox hydraulic pump)
FAQS on gearbox hydraulic pump
Q: What is the primary function of a Hydraulic Gear Pump?
A: A Hydraulic Gear Pump transfers fluid by using interlocking gears to generate flow. It converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy, powering systems like machinery or vehicles. Its efficiency depends on gear precision and fluid viscosity.
Q: How does a Hydraulic Cylinder interact with a Hydraulic Gear Pump?
A: The Hydraulic Gear Pump supplies pressurized fluid to the Hydraulic Cylinder, enabling linear motion. The cylinder converts hydraulic energy into mechanical force, essential for lifting or pressing. Proper pressure regulation ensures optimal performance.
Q: What are common maintenance steps for a Hydraulic Motor?
A: Regularly check fluid levels, filters, and seals for wear or contamination. Ensure proper alignment with connected components like the Hydraulic Gear Pump. Monitor temperature and pressure to prevent overheating or leaks.
Q: Can a Hydraulic Gear Pump be used with multiple Hydraulic Motors?
A: Yes, but it requires a system design with flow dividers or priority valves. Uneven load distribution may affect efficiency. Consult specifications to ensure compatibility and avoid overloading the pump.
Q: What causes noise in a Hydraulic Gear Pump?
A: Noise often stems from cavitation, air ingress, or worn gears. Low fluid levels or clogged filters can restrict flow, increasing vibration. Regular maintenance and using recommended fluids reduce operational noise.
-
Understanding Flow Dividers HydraulicNewsMay.16,2025
-
Power Steering Unit CostNewsMay.16,2025
-
Essential Components for Power TransmissionNewsMay.16,2025
-
Essential Components for Fluid ControlNewsMay.16,2025
-
Best Castings for SaleNewsMay.16,2025
-
Understanding Plum Blossom Couplings and Their PurposeNewsMay.14,2025
-
Understanding Couplings and Their ImportanceNewsMay.14,2025















